本文是我在学习候捷《STL标准库和泛型编程》课程时所做的笔记,在此分享给大家。
STL源码剖析
命名空间
所有新式header的组件,都封装于“std”命名空间下。
STL六大件
容器(Container)、算法(Algorithm)、分配器(Allocator)、迭代器(Iterator)、适配器(Adapter)、仿函数(Functor)
关系
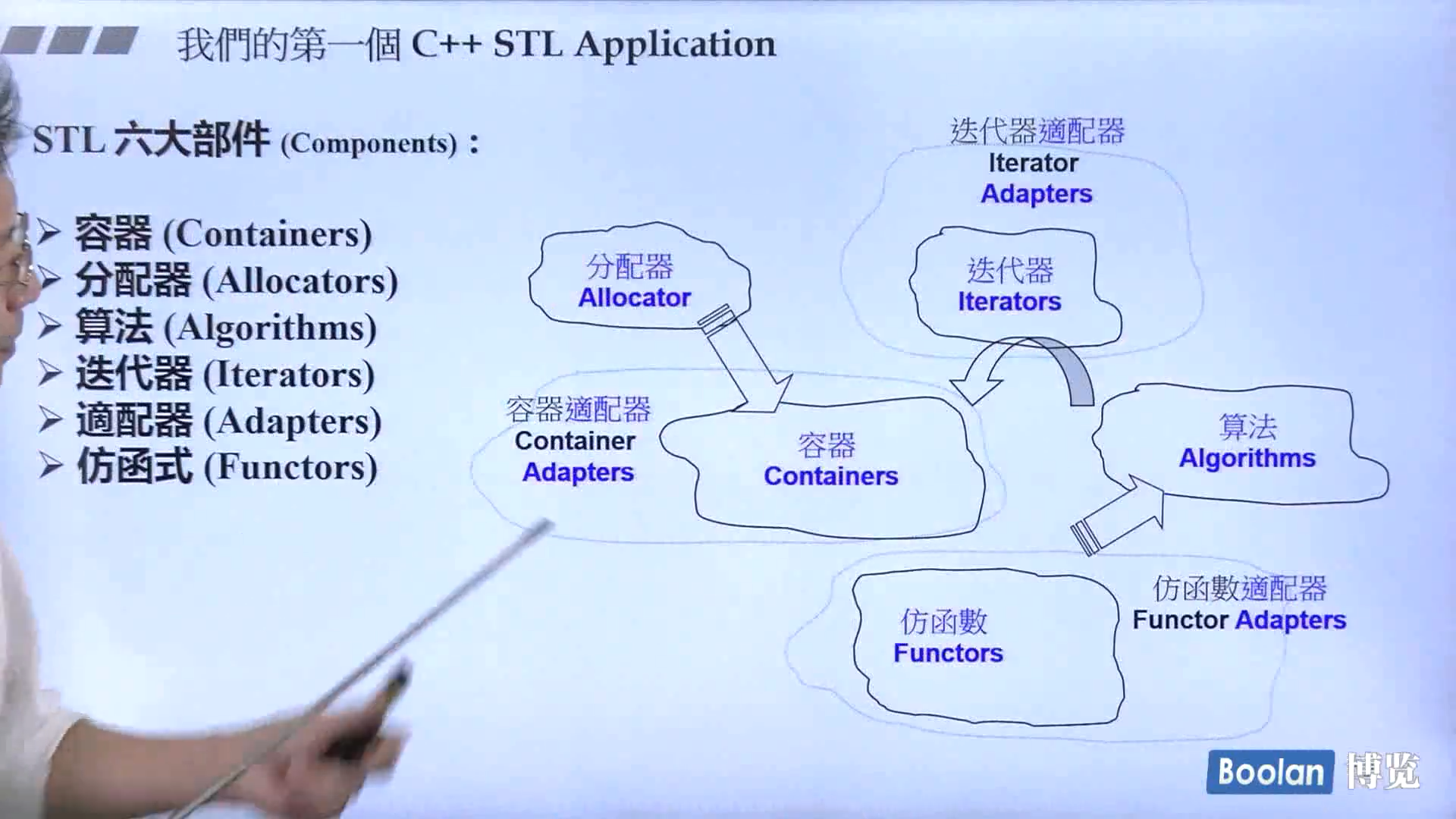
1
2
3
4
| int ia[6] = {2, 52, 365, 37, 587, 23};
vector<int, allocator<int>> vi(ia, ia + 6);
cout << count_if(vi.begin(), vi.end(), not1(bind2nd(less<int>(), 40)));
|
vector容器。allocator<int>分配器。vi.begin()迭代器。count_if()算法。not1仿函数适配器。less<int>()仿函数。bind2nd(a,b)适配器,绑定第二参数。not1()适配器,否定相应内容。
not1(bind2nd(less<int>(), 40))predicate,判断条件。
x.begin(),x.end()维持的是左闭右开区间,x.end()指向最后一个元素的下一位置。
迭代器遍历
1
2
| Container<T> c;
for(Container<T>::iterator iter = c.begin(); iter!=c.end(); ++iter)
|
容器分类
红色部分为C++11新特性。
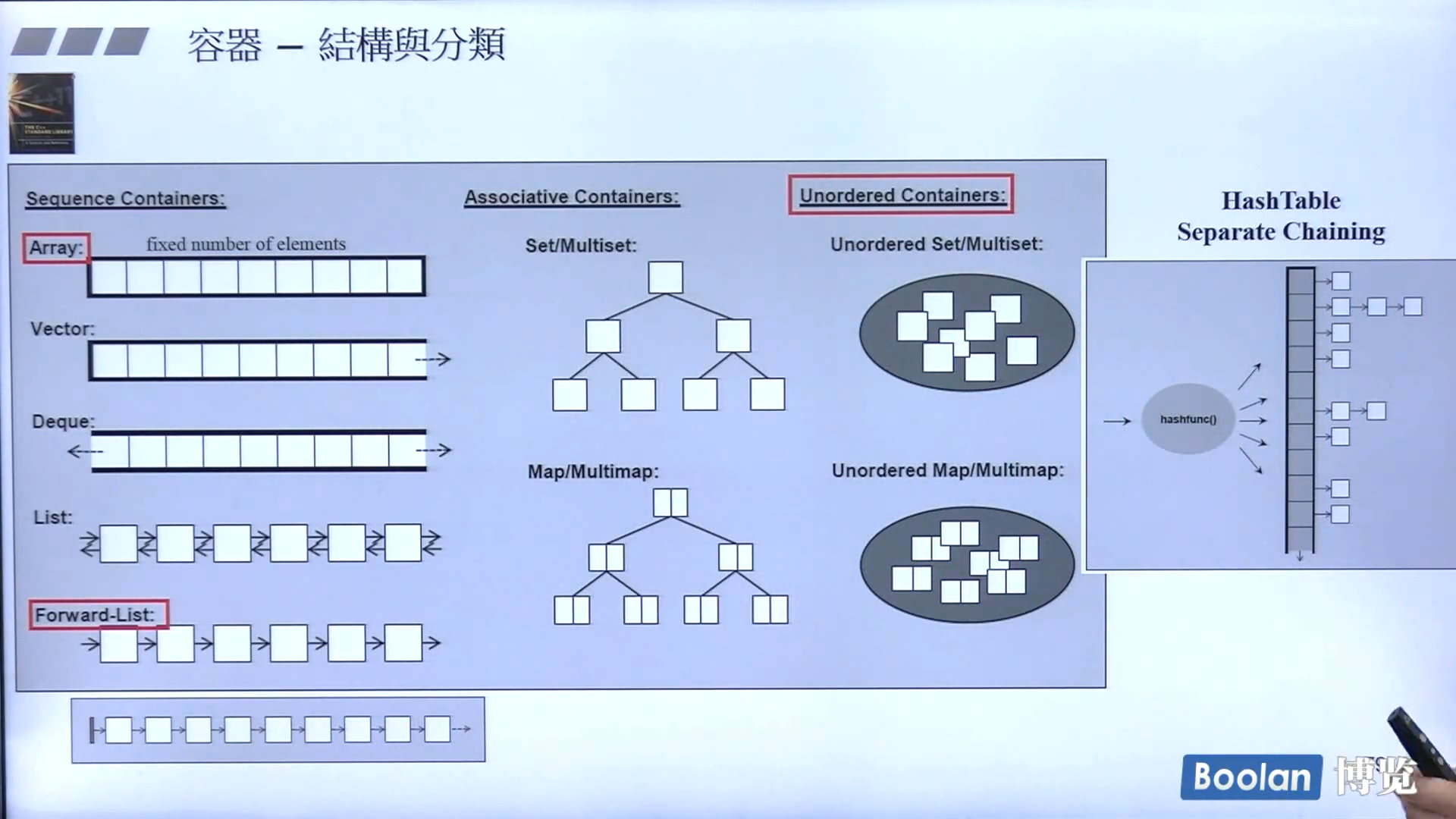
顺序型容器
array
只是将数组封装成class。
size()、front()、back()可用
声明
1
2
3
| array<type,SIZE> arr;
arr.data()
|
vector
变长数组(尾部可变)
deque
两端可扩。是分段连续的。
每段一个buffer,每个buffer可以存储一定的元素(满,进入下一个buffer),buffer两端可扩展。
list
双向链表。
forward-list
单链表。单链表没有push_back(),而是push_front()
1
2
3
| forward_list<int> fl;
fl.push_front(1);
fl.pop_front();
|
容器适配器
由deque封装而来。
queue
stack
关联式容器
key-value。通过key找value。查找更方便。
multikey可重复。unordered迭代器易失效。
set/multiset
底层红黑树。每个节点key即为value。
map/multimap
底层红黑树。除key之外有value。
unordered set/multiset
底层链式防冲突哈希表。每个节点key即为value。
unordered map/multimap
底层链式防冲突哈希表。除key之外有value。
分配器
在定义时候,带有默认值。可以不声明。以vector为例。
1
2
3
4
| template <typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp>>
class vector : protected_Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc>{
...............
}
|
OOP vs GP
面向对象编程(OOP)企图将数据(data)和方法(method)关联一起。
泛型编程(GP)企图将数据(data)和方法(method)分开。
GP可以将容器和算法各自分开开发,通过iterator连接即可。(操作符重载显得很重要)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| template<typename _Tp, typename _Compare>
inline const _Tp&
max(const _Tp& __a, const _Tp& __b, _Compare __comp)
{
if (__comp(__a, __b))
return __b;
return __a;
}
|
STL源码基础
运算符重载
:: . .* ?:这四个运算符不能够重载
模板
主要用到的是类模板、函数模板。除此之外,还用到了特化。
特化之前要有template<>
分配器
operator new & malloc
内存分配的底层都是调用operator new 然后调用malloc。通过malloc,调用操作系统的api。
malloc所申请的内存,除所申请的内存外还有一些附加的额外开销。(因为释放时只传入指针,通过这些附加属性可以找到需要释放的地址。)
容器
set里面复合红黑树,非继承。两侧表示相应的sizeof大小,至于容器中存的元素多少,与容器大小无关。
下图中缩进表示复合关系。

list
为了使迭代器更好的自增自减,一般均设计为类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| template<typename T>
struct list_node {
typedef void *void_pointer;
void_pointer prev;
void_pointer next;
T data;
};
template<typename T,class Alloc = alloc>
class list {
protected:
typedef list_node<T> list_node;
public:
typedef list_node *link_type;
typedef list_iterator<T, T &, T *> iterator;
private:
link_type node;
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator {
typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
typedef T value_type;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef list_node<T> *link_type;
link_type node;
reference operator*() const {
return (*node).data;
}
pointer operator->() const {
return &(operator*());
}
}
|
其中需要特别注意的是,很多运算符已经重载,在阅读过程中要注意其功能及调用次序。
根据运算符的性质,考虑其返回值类型。(前置++传回引用,后置++传值)。
list底层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| struct _List_node_base {
_List_node_base* _M_next;
_List_node_base* _M_prev;
};
struct _List_node : public _List_node_base {
_Tp _M_data;
}
struct _List_iterator_base {
_List_node_base* _M_node;
};
class _List_base
{
protected:
_List_node<_Tp>* _M_node;
};
class list : protected _List_base<_Tp, _Alloc> {
}
|
iterator遵循的原则
trait,萃取。
algorithm要知道iterator的一些属性。 iterator共五种associated type。分别为(后面两种没有被使用过)
- iterator_category
- difference_type
- value_type
- reference
- pointer
以链表为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_iterator
{
typedef _List_iterator<_Tp> _Self;
typedef _List_node<_Tp> _Node;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef std::bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
};
|
算法调用时,根据访问相应的类别,获取到相应的类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| template <typename I>
algorithm(I first,I last) {
I::iterator_category
I::difference_type
I::value_type
I::pointer
I::reference
}
|
如果传入的iterator不是class(比如指针),通过萃取机(中间件)获得相应的类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| template<typename _Iterator>
struct iterator_traits
{
typedef typename _Iterator::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename _Iterator::value_type value_type;
typedef typename _Iterator::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename _Iterator::pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Iterator::reference reference;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| template<typename _Tp>
struct iterator_traits<_Tp*>
{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
};
template<typename _Tp>
struct iterator_traits<const _Tp*>
{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef const _Tp* pointer;
typedef const _Tp& reference;
};
|
vector
vector 内部封装了三个迭代器start,finish,end_of_storage。
当容器填满时,在内存中分配另外一块两倍大小的空间。(造成迭代器失效)
deque
分段连续。内部有start、finish迭代器用来控制map(控制中心)首尾,map中的元素指向相应的buffer。buffer里存放具体的数据。为了维持连续这一假象,当触及到buffer边界时,会扩充。除此之外,内部还有map_size来判断大小。
__deque_buf_size存在默认值,每个缓冲区大小为512字节,然后根据参数类型改变缓冲区可以存储的元素个数。
1
2
3
| inline size_t __deque_buf_size(size_t __size) {
return __size < 512 ? size_t(512 / __size) : size_t(1);
}
|
deque的构成:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| class deque{
protected:
iterator start;
iterator finish;
map_pointer map;
size_type map_size;
};
|
基本操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| reference front()
{return *start;}
reference back()
{
iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return *tmp;
}
size_type size()const
{return finish - start;}
bool empty() const
{return finish == start;}
|
deque迭代器
1
2
3
4
5
6
| class deque_iterator{
Elt_pointer cur;
Elt_pointer first;
Elt_pointer last;
Map_pointer node;
}
|
模拟连续空间
模拟连续空间主要是由deque_iterator实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
| reference operator*() const {
return *cur;
}
pointer operator->() const {
return &(operator*());
}
|
两个iterator之间距离:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| difference_type operator-(const self& x) const {
return difference_type(buffer_size()) *(node - x.node - 1) + (cur - first) + (x.last - x.cur);
}
|
++/–
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| void set_node(map_pointer new_node) {
node = new_node;
first = *new_node;
last = first +difference_type(buffer_size());
}
self & operator++() {
++cur;
if(cur == last) {
set_node(node + 1);
cur = first;
}
return *this;
}
self operator++(int) {
self tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
self & operator--() {
if(cur == first) {
set_node(node - 1);
cur = last;
}
--cur;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int) {
self tmp = *this;
--*this;
return tmp;
}
|
+=/-=
首先判断移动后的位置会不会跨越缓冲区边界。跨越则寻找合适位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| self& operator+=(difference_type n) {
difference_type offset = n + (cur - first);
if (offset >= 0 && offset < difference_type(buffer_size())) {
cur += n;
} else {
difference_type node_offset = offset > 0 ? offset / difference_type(buffer_size()) : -difference_type((-offset - 1) / buffer_size()) - 1;
set_node(node + node_offset);
cur = first + (offset - node_offset * difference_type(buffer_size()));
}
return *this;
}
self operator+(difference_type n) const {
self tmp = *this;
return tmp += n;
}
self &operator-=(different_type n) {
return *this += -n;
}
self operator-(different_type n) const {
self tmp = *this;
return tmp -= n;
}
reference operator[] (different_type n) const {
return *(*this + n);
}
|
stack/queue
底层容器可以是deque/list。此外,stack还可以选择vector作底层容器。默认是deque,在此基础上封装,调用deque去实现。
stack/queue不提供iterator,不允许遍历。
RB_tree
自平衡二叉搜索树。数据排列规则有利于插入和查找;
rb_tree提供遍历功能。使用++遍历得到的结果是有序的(sorted)
不推荐rb_tree的iterator改值。(破坏排序规则)
- 但并非编程层面禁止。
rb_tree服务于map/set,而map允许改value值。
rb_tree提供两种插入insert_unique()和insert_equal()。表示是否允许key值重复。(multi)
以下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| template <class Key,
class Value, //value = key + data
class KeyOfValue, //在value中捕获key的方式
class Compare, //key比较方式
class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree {
protected:
typedef rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
public:
typedef rb_tree_node *link_type;
protected:
size_type node_count;
link_type header;
Compare key_compare;
};
rb_tree<int, int, identity<int>, less<int>, alloc> TreeNode;
template<class T>
struct identity : public unary_function<T,T> {
const T &operator()(const T &x) const { return x; }
};
template<class T>
struct less :public binary_function<T,T,bool> {
bool operator()(const T &x, const T &y) const {
return x < y;
}
};
|
一个红黑树节点包括3ptr+1 enum =24 Bytes
3ptr:parent、right、left
set/multiset
set/multiset以rb_tree为底层,元素会自动排序(依据key)。- 禁止通过iterator改值。
- set所有操作都对底层红黑树进行操作。可以理解为容器适配器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| template <class Key,
class Compare = less<Key>,
class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;
typedef Compare key_compare;
typedef Compare value_compare;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, identity<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t;
public:
typedef typename rep_type::const_iterator iterator;
};
|
map/multimap
- 以
rb_tree为底层,元素会自动排序(依据key)。
- 禁止通过iterator改
key值,但可以改data()通过将key_type指定为const实现。
- map中可以用operator[]访问。存在,则修改
data或访问。否则,创建节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| template <class Key,
class T,
class Compare = less<Key>,
class Alloc = alloc>
class map {
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef T data_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
typedef Compare key_compare;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t;
public:
typedef typename rep_type::iterator iterator;
};
|
hashtable
哈希冲突时再哈希时间复杂度过高,采用链式存储解决此问题。
每个Hash(x)值为一个bucket。
当元素个数超过bucket个数时,rehash。bucket个数通常为质数,每次扩充约为2倍。
可以通过iterator改data,但不能改key。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| template <class Value>
struct __hashtable_node {
__hashtable_node *next;
Value val;
};
template <class Value,
class Key,
class HashFcn,
class EXtractKey,
class EqualKey,
class Alloc = alloc>
struct __hashtable_iterator {
node *cur;
hashtable *ht;
};
template <class Value,
class Key,
class HashFcn, //哈希映射
class EXtractKey, //在所存取的数据中取key
class EqualKey, //给定元素比对的原则
class Alloc = alloc>
class hashtable {
public:
typedef HashFcn hasher;
typedef EqualKey key_equal;
typedef size_t size_type;
private:
hasher hash;
key_equal equals;
EXtractKey get_key;
typedef __hashtable_node<Value> node;
vector<node *, Alloc> buckets;
size_type num_elements;
public:
size_type bucket_count() const {
return buckets.size();
}
};
|
modulus运算
通过计算得出元素该存放在哪个bucket。
c++11开始,hashtable_xxx更名为unordered_xxx。
迭代器
迭代器共五种
1
2
3
4
5
| struct input_iterator_tag {};
struct output_iterator_tag {};
struct forward_iterator_tag: public input_iterator_tag{};
struct bidirectional_iterator_tag: public forward_iterator_tag{};
struct random_access_iterator_tag: public bidirectional_iterator_tag{};
|
调用时根据萃取机获取迭代器的类型(iterator_category)然后进行相应的调用。
不同类型的迭代器对元素访问的方式也不同,因此迭代器类型不同,可能会对算法有影响
样例如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| template<class InputIterator>
inline iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type distance(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,input_iterator_tag) {
typedef typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::iterator_category category n = 0;
while (first != last) {
++first;
++n;
}
return n;
}
template<class RandomAccessIterator>
inline iterator_traits<RandomAccessIterator>::difference_type _distance(RandomAccessIterator first,RandomAccessIterator last, random_access_iterator_tag) {
return last - first;
}
template<class InputIterator>
inline iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type distance(InputIterator first,InputIterator last) {
typedef typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::iterator_category category;
return _distance(first, last, category());
}
|
由于上述算法只对input_iterator 和random_access_iterator进行了实现,当使用其他类型的迭代器(如forward_iterator)进行调用时,由于forward_iterator继承自input_iterator,故调用对input_iterator实现的函数。
算法
标准库中所有的Algorithm都看不见Container,而是通过iterator进行操作。
Algorithm一定需要传入首尾两个迭代器。
xxx,xxx_if,xxx_copy(如replace,replace_if)前一个是一个默认条件,xxx_if支持自己给出一个条件,xxx_copy不会改原值,而是返回一个新创建的序列。
仿函数
又叫函数对象,服务于算法。仿函数分类:
- 算术类:plus(+)、minus(-)
- 逻辑运算类:logical_and
- 相对关系类:equal_to、less
GNU C++(GCC)有一些独有的仿函数:identity、select1st、select2nd。(非标准库)
Adapter
适配器、改造器。可分为容器适配器、迭代器适配器、仿函数适配器。修改一些对外的接口,使得相应的组件能够适配。
仿函数适配器
binder2nd
bind2nd为辅助函数,其底层仍为binder2nd。绑定第二实参。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| template<typename _Operation>
class binder2nd
: public unary_function<typename _Operation::first_argument_type,
typename _Operation::result_type>
{
protected:
_Operation op;
typename _Operation::second_argument_type value;
public:
binder2nd(const _Operation& __x,
const typename _Operation::second_argument_type& __y)
: op(__x), value(__y) { }
typename _Operation::result_type
operator()(const typename _Operation::first_argument_type& __x) const
{ return op(__x, value); }
typename _Operation::result_type
operator()(typename _Operation::first_argument_type& __x) const
{ return op(__x, value); }
} _GLIBCXX_DEPRECATED;
|
typedef typename xxx xx中的typename主要用于告诉编译器xxx的类型,以方便编译器能够更好的识别。
现版本的binder2nd、binder1st被bind替代。
not1
1
2
| template< class Predicate >
constexpr std::unary_negate<Predicate> not1(const Predicate& pred);
|
用于创建函数对象的辅助函数,该函数对象返回所传递的一元(同理,not2创建的是二元)谓词函数的补码。
一元、二元
元表示的是操作数的个数。一元(unary)如less(<xxx)。二元(binary)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| template<class _Arg,class _Result>
struct unary_function
{
typedef _Arg argument_type;
typedef _Result result_type;
};
template<class _Arg1,class _Arg2,class _Result>
struct binary_function
{
typedef _Arg1 first_argument_type;
typedef _Arg2 second_argument_type;
typedef _Result result_type;
};
|
bind
取代了bind1st,bind2nd。可以绑定函数、仿函数、成员函数、成员变量。 返回值是仿函数。
以除法为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| double divide(double x,double y) {
return x/y;
}
auto x1 = bind(divide,a,b);
cout << x1();
auto x2 = bind(divide,_1,b);
cout << x2(x);
auto x3 = bind(divide,_2,_1);
cout << x3(x,y);
auto x4 = bind<int>(···)
|
bind()绑定成员变量时,有一个隐藏的参数this指针
迭代器适配器
reverse_iterator
1
2
| reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(end());}
reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(begin());}
|
在实现具体使用时,对逆向后的迭代器取值相当于把正向迭代器退一格取值。reverse_iterator的++、--、+n、-n也要逆序
inserter
以第三参数传入,调用相应的运算符重载,在数组中指定位置插入相应的新数据(后面的数据会后移)
ostream_iterator
可以简化输出过程。利用ostream_iterator。现有一个数组
1
2
3
4
| vector<int>arr{1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
ostream_iterator<int> temp(cout,",");
copy(arr.begin(),arr.end(),temp);
|
cout是输出流,ostream_iterator将指定内容写入流中。
istream_iterator
输入流。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| istream_iterator<double>eos;
istream_iterator<double>iit(cin);
if(iit!=eos)
value1=*iit;
++iit;
if(iit!=eos)
value2=*iit;
cout<<value1 <<"*"<<value2<<"="<<value1*value2;
|
tuple
指定任意类型的任意元素。类似于一个临时创建的结构体。
1
2
3
| tuple<int,double,string>t1(41,6.3,"niko");
auto t2 = make_tuple(41,25,"zzz");
get<0>(t1);
|
tuple可以赋值、比较(相同类型依次比较元素)、直接cout输出。
tuple_size可以知道元素的个数
tuple_element可以知道元素的类型
利用可变模板元来实现的tuple。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| template<typename... Values>class tuple;
template<>class tuple<>{};
template<typename Head,typename... Tail>
class typle<Head,Tail...>:private tuple<Tail...>{
typedef tuple<Tail...>inherited;
public:
tuple(){}
tuple(Head v, Tail... vtail):m_head(v),inherited(vtail...){}
typename Head::type head() {return m_head;}
inherited& tail {return &this;}
protected:
Head m_head;
};
|
每次分为.当最终没有参数时,执行tuple<>结束.
type traits
将功能相同而参数不同的函数进行抽象
通过traits将不同的参数的相同属性提取出来,在函数中利用这些用traits提取的属性,使得函数对不同的参数表现一致。故,可实现在编译期计算、判断、转换、查询等等功能。
c++为默认数据类型都提供了相应的类型萃取机制,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| template<> struct __type_traits<int>{
typedef __true_type has_trivial_default_constructor;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_assignment_operator;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_destructor;
typedef __true_type is_POD_type;
};
|
is_void
去除掉const和volatile之后返回类型。然后调用相应的辅助函数,如果有相应的参数(偏特化),则返回true,否则返回false。
进而扩展is_class、is_union、is_enum、is_pod,但并没有找到。
cout
cout对<<运算符的各种输入进行重载,以实现可以随意输出。


